Machine Translation (MT) technology has emerged as a crucial enabler of global communication and knowledge sharing in our increasingly interconnected world. As we approach a milestone of 6.04 billion internet users globally, representing 73.2% of the world's population, the need for effective cross-lingual communication has never been more critical. This article explores why machine translation matters and how it revolutionizes knowledge sharing, access, communication, and information gathering in our interconnected world.

The Digital 2025 October Global Statshot Report reveals that “finding information” remains the primary reason why people use the internet today. A task that is significantly compromised if not done in a major language.
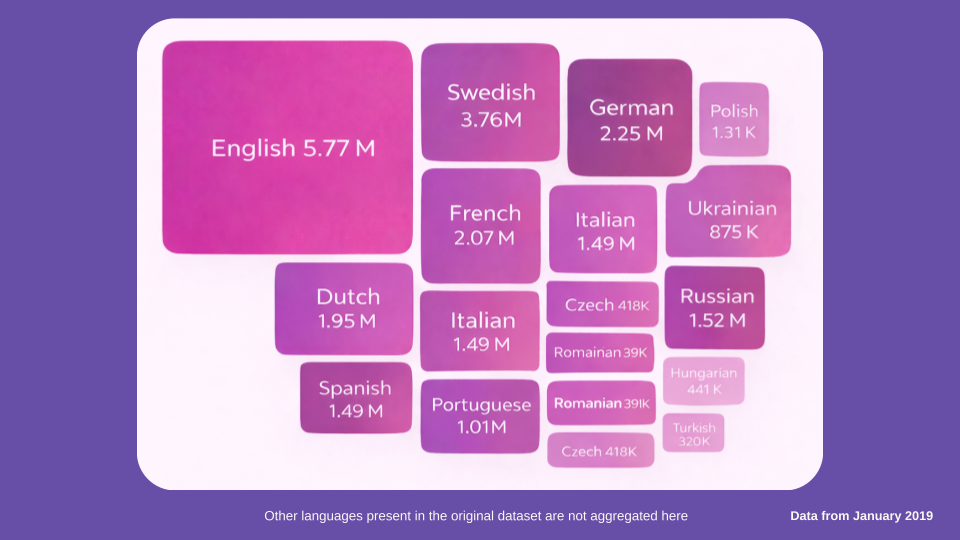
If we take Wikipedia as a rough proxy for freely available high-quality information in a language, we can see that the size of the English-language Wikipedia—as measured by the number of articles, the number of words, and the size of the database, among other aspects—is much larger than other languages. As of 2019 (the latest data available), the English-language Wikipedia was still three times larger than the next-largest languages, German and French.
The chart below gives a rough idea of the linguistic distribution of “open-source knowledge” by language group and shows the concentration of available resources by language. The linguistic imbalance is easy to see in the cartogram below, which shows the article count of European Wikipedias by language family. Article count is represented by size, and language family by color.
The Global Imperative for Machine Translation
We face unprecedented global challenges that require collaborative solutions across linguistic boundaries. Climate change, pandemic management, and poverty reduction—the three most pressing global problems we face today—demand cooperation, collaboration, and communication among diverse groups worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic and increasingly frequent climate-related disasters clearly demonstrate that isolated efforts at a national level are insufficient; we need coordinated global responses.
Machine-translation technology has evolved dramatically in recent years, moving from rudimentary word-for-word translations to sophisticated neural systems capable of producing increasingly fluent and accurate translations. These advancements are timely as the information landscape continues to expand exponentially. The bulk of this information originates in just a few key languages, creating a potential global digital divide.
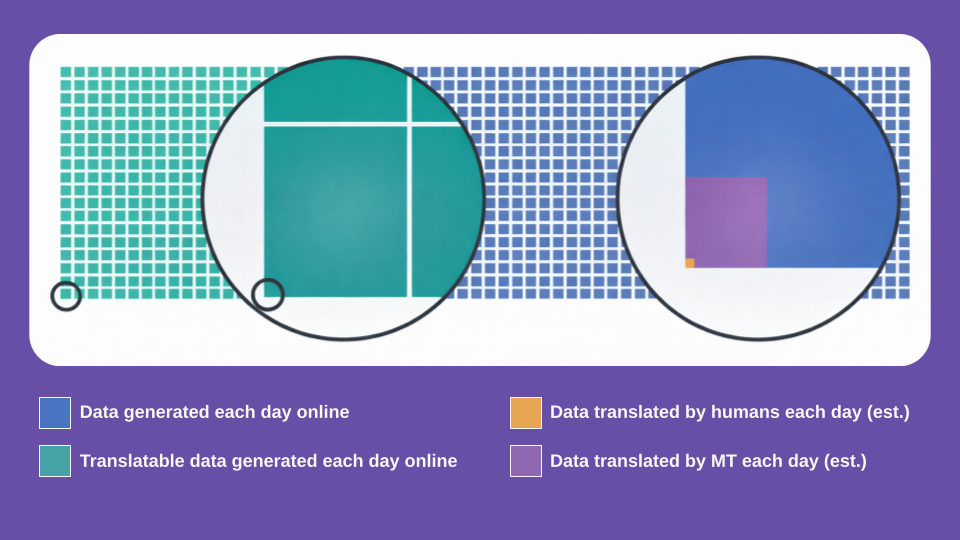
CSA Research estimates that approximately 34 exabytes of data are generated daily worldwide. The graphic below provides a proportional view of the total data generated online each day, represented in blue. The green section illustrates how much of this data is textual and therefore translatable. In 2025, we translated less than a single green square.
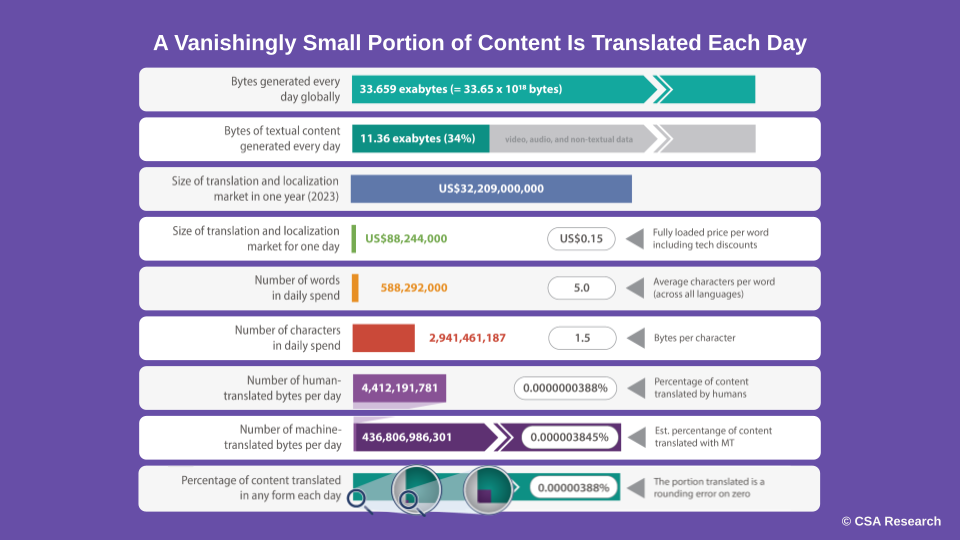
CSA Research estimates that around 34 exabytes of data are generated daily across the world, of which about 11.36 exabytes is textual content. They point out that a minuscule portion of this textual content is translated; 99% by machine translation and less than 1% by humans! They estimate that only 0.00000389% of the textual content created daily is translated.
This suggests that the latent demand for effective translation technology is significant and that we have only just begun to address the needs of emerging markets in accessing, sharing, and communicating with digitally dominant populations.
The future demand for human translation is quite possibly 100X or more of what it is today, and the demand for effective, high-quality machine translation may be 1,000X or more of current usage!
Knowledge Sharing Across the Digital Language Divide
The digital world faces a significant language imbalance, with English dominating online content despite the diversity of global internet users. This creates substantial barriers for non-English speakers, limiting their access to digital resources and information. Machine translation serves as a crucial bridge across this divide, democratizing access to information and enabling truly global communication.
Machine translation serves as a powerful enabler for sharing institutional knowledge across industries, governments, and scientific communities. In the academic and research community, MT plays a vital role in enabling collaboration and knowledge sharing. Researchers from different countries and language backgrounds can access scientific articles, conference proceedings, and research findings through translated versions. This CSA Researchaccelerates scientific progress and facilitates interdisciplinary collaborations that might otherwise be impossible.
The incorporation of machine translation enables seamless communication between teams and partners operating in different countries who speak different languages. It eliminates the need for lengthy translation processes, allowing for real-time information exchange. This is particularly critical when transmitting country-specific knowledge and know-how, as the risk of failure to transfer specialized information becomes significant when language barriers exist.
Consider the potential impact in healthcare: The World Health Organization estimates that 15 million babies are born prematurely each year, with complications being the leading cause of death among children under five. According to the University of Limerick, "80% of the premature deaths in the developing world are due to lack of information." Machine translation can help bridge this critical knowledge gap, making life-saving medical information accessible across language barriers.
The business sector has witnessed a revolutionary transformation in how institutional knowledge is shared across borders. Major e-commerce platforms like Alibaba now translate up to 500 billion words daily to support global customer interactions, demonstrating the massive scale at which MT facilitates business operations. This capability enables:
- Seamless transfer of technical documentation
- Global training and development programs
- Cross-border customer support
- International team collaboration
One of the most profound impacts of machine translation is its ability to democratize access to information. Much of the world's knowledge is created and remains in a handful of languages, inaccessible to those who don't speak these languages.
This disparity creates what can be called "information poverty." As Ethan Zuckerman eloquently stated, "For the internet to fulfill its most ambitious promises, we need to recognize translation as one of the core challenges to an open, shared, and collectively governed internet." Machine translation offers a way to reduce this digital divide and potentially raise living standards across the world.
Cross-language information-retrieval systems are revolutionizing how people access knowledge across linguistic boundaries. These systems enable users to search for information in one language and retrieve relevant results in multiple languages by translating queries or documents. By incorporating contextual understanding and semantic analysis, these tools capture nuances and cultural references that might otherwise be lost in translation.
Enhancing Real-Time Communication
Machine translation is transforming how we communicate across language barriers in both formal and informal contexts. Real-time translator applications now allow users to enter into conversations around the world through innovative instant-translation tools. These systems can automatically detect the language being spoken, translate it in real time, and even maintain the speaker's voice characteristics.
The technology behind real-time speech-to-speech translation combines several sophisticated components: speech recognition to transcribe what's being said, machine translation to convert it to another language, and voice synthesis to generate speech that sounds natural and matches the speaker's voice characteristics. This technology enables seamless conversations between people who don't share a common language, opening up new possibilities for international business, diplomacy, and personal connections.
In the business context, AI-powered translation facilitates global collaboration across diverse teams and cultures. Whether it's multinational corporations conducting business negotiations, international research teams collaborating on groundbreaking projects, or individuals connecting with others from different parts of the world, MT enables seamless communication regardless of language differences.
Government and Public Sector Communication
In the public sector, MT plays a vital role in facilitating communication between governments and citizens. Studies on cross-boundary information systems within public-sector organizations highlight how MT technologies enable effective knowledge sharing.
. This has become particularly important for:
- Disseminating public policy information
- Providing multilingual citizen services
- Supporting international cooperation
- Enabling emergency communications across language barriers
Scientific and Academic Exchange
The scientific community has embraced MT as a crucial tool for global knowledge dissemination.
The emphasis on Open Innovation in Science
demonstrates how MT supports:
- International research collaboration
- Access to global scientific literature
- Cross-border technology transfer
- Multilingual academic conferences and publications
Transforming Audiovisual Content
- As content delivery increasingly shifts toward video and audio formats, machine translation's role in making this content accessible across languages becomes more critical. Educational institutions, entertainment providers, and businesses are leveraging MT to reach global audiences through translated audiovisual content.
- Real-time speech-to-speech translation technology is advancing rapidly, allowing for the translation of video content while preserving the speaker's voice characteristics. This technology combines speech recognition, machine translation, and voice synthesis to create an experience where viewers can watch content in their preferred language while still hearing the original speaker's voice and intonation patterns.
- For educational content, this means students worldwide can access lectures, tutorials, and instructional videos regardless of the original language. For businesses, it enables global training programs, international presentations, and multilingual marketing campaigns without the need for multiple versions of the same content.
Information Gathering and Social Media Monitoring
- In today's digital world, valuable insights often emerge from conversations happening across social media platforms in multiple languages. Multilingual sentiment analysis—the AI-driven process of extracting sentiment from data containing several languages—allows organizations to monitor and understand these conversations at scale.
- This technology involves sophisticated processes, including part-of-speech tagging, lemmatization, understanding grammatical constructs, and determining the polarity of words to give an overall sentiment assessment. Importantly, these models must be native to each language rather than applying English-language rules to multilingual data, which would yield incorrect insights.
- Multilingual social listening enables brands to track and analyze social media conversations in multiple languages, providing insights into target audience preferences, attitudes, and behaviors. This capability is crucial for reputation management, understanding market trends, and identifying emerging issues across different cultural and linguistic contexts.
Enabling Cross-Cultural Entertainment and Social Interaction
Machine translation is breaking down barriers in entertainment and casual social media interactions. With real-time translation capabilities, people can engage with content creators, follow discussions, and participate in communities regardless of language differences. This democratization of social media enables rich cultural exchanges and global community building that was previously impossible.
Language barriers? No more! Users can enter into conversations around the world thanks to innovative instant-translation tools that support over 45 languages. These tools allow users to improve their communication skills, immerse themselves in new cultures, and bridge gaps between different worlds.
The ability to automatically translate social media posts, comments, and messages enables truly global conversations around shared interests, from entertainment and sports to politics and social causes. This capability not only enhances individual experiences but also contributes to greater cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
The Challenge of Low-Resource Languages
Despite tremendous progress in machine translation, significant challenges remain, particularly for low-resource languages with limited available bilingual data for training MT systems. Currently, there are around 7,111 known languages and dialects in the world, with the European Union alone accounting for more than 200 of them. However, high-quality MT systems only exist for a small fraction of these languages.
Researchers are addressing this challenge through several innovative approaches:
- 1. Human-driven data collection through coordinated efforts from governments, academia, the scientific community, and humanitarian initiatives.
- 2. Massively multilingual MT approaches where large groups of language pairs (10–200) are trained together, allowing data from high-resource language pairs to improve the quality of low-resource languages.
- 3. Use of monolingual data to supplement limited bilingual data, enabling MT development for the "long tail" of languages.
Recent breakthroughs include Meta's No Language Left Behind (NLLB) model, which can translate 200 different languages, including many low-resource ones. This system performs 44% better than pre-existing systems and includes three times as many low-resource languages as high-resource languages. Such technologies could help people speaking rarely translated languages to access the internet and other technologies, with education a particularly significant application.
The Future: Human-Machine Collaboration
As machine translation continues to improve, the most effective approach appears to be collaboration between humans and machines rather than complete automation. While AI can handle large volumes of text and ensure technical consistency, it still lacks the cultural sensitivity and creativity needed to translate and resonate with a target audience.
NMT has demonstrably improved translation quality over its predecessors, often achieving impressive levels of fluency. However, it is crucial to recognize that MT is not yet a flawless substitute for expert human translators, especially in contexts requiring utmost accuracy, cultural nuance, or creative linguistic expression. The initial goal for MT was often to produce output that was comprehensible enough for human translators to understand the meaning and efficiently refine the text. Linguistic AI systems, including MT, can sometimes generate output that is incorrect, nonsensical, or biased—phenomena sometimes described by critics using terms like "stochastic parrots," highlighting that these systems operate on patterns without genuine understanding or cognition. Consequently, robust human-in-the-loop processes, where human experts review and correct MT output, are indispensable for quality assurance in many real-world applications, particularly when the stakes are high. The future improvements in translation technology are more likely to empower and augment human experts rather than replace them.
Translated SRL has provided compelling evidence of continuous quality improvements in MT over time. Their measurements, taken over several years by monitoring the behavior of over 100,000 expert translators correcting two billion sentence segments across many domains and languages, demonstrate relentless MT quality progress in professional MT use.
This formalization of an active and collaborative relationship between humans and machines is increasingly important. The human-in-the-loop process that provides rapidly assimilated and learned corrective feedback from experts will be a crucial element of any truly useful AI initiative in the future.
Lara represents a significant advancement in AI-driven translation, building upon ModernMT's established reputation and experience, for superior MT quality and adaptability. By leveraging a human-optimized approach that integrates specialized data and actively captures corrective feedback, it achieves superior fluency and naturalness, often approaching the quality and nuance of human translation.
Lara is a next-generation automated translation technology that is a major step forward from the static, minimal-control MT experience of the past. It enables straightforward and rapid incorporation of context and style.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Machine-translation technology is not merely a convenience but a necessity in our globally connected world. It enables knowledge sharing across industries and borders, democratizes access to information, facilitates real-time communication, transforms audiovisual content, enhances information gathering, and enables cross-cultural entertainment and social interaction.
As the technology continues to advance, particularly for low-resource languages, its impact will only grow. The most successful implementations will likely involve collaboration between humans and machines, combining the scalability and efficiency of AI with human cultural understanding and creativity.
In addressing global challenges like climate change, pandemic management, and poverty reduction, machine translation will play an increasingly vital role in enabling the kind of international collaboration necessary for success. By breaking down language barriers, MT technology helps create a more equitable world where knowledge and opportunity are not limited by the language a person speaks.
As the visionary Ethan Zuckerman has noted, mass machine translation should not be seen as a translation of individual texts, but as liberating the discovery of knowledge from the constraints of language. In this sense, machine translation is not just about converting words from one language to another—it's about unleashing human potential on a global scale. The technology's impact extends beyond mere translation, fostering global understanding, enabling cross-cultural exchange, and supporting the development of a truly connected global community. As MT continues to evolve and improve, its role in facilitating global communication and knowledge sharing will become even more central to our increasingly digital and multilingual world.
Ultimately, the trajectory of machine translation should be guided not solely by technological advancement but by the overarching goal of enhancing human connection and enabling shared purpose across diverse cultures and languages. As MT systems continue to learn, adapt, and improve—ideally in close collaboration with human experts—they will become increasingly invaluable assistants, empowering humanity to communicate more effectively, share knowledge more broadly, and work together more cohesively to address the complex global challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
